Activity objects represent a metafor for allocation of locus-of-control in DUECA. More...
#include <Activity.hxx>
Public Types | |
| enum | RunState { Off , Last , Ready , Braking , Running , ReadyWork , FirstWork , RunningWork , BrakingWork , LastWork } |
| To track the run state, and signal about first/last/work etc. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| Activity (const GlobalId &owner, const char *my_name, const PrioritySpec &s) | |
| Constructor. | |
| virtual | ~Activity () |
| Destructor. | |
| void | switchOn (const TimeTickType &time=0) |
| Specify the time from which the Activity is switched on. | |
| void | switchOff (const TimeTickType &time=0) |
| Specify the time when this Activity should be switched off. | |
| void | switchOn (const TimeSpec &time) |
| Specify the time from which the Activity is switched on. | |
| void | switchOff (const TimeSpec &time) |
| Specify the time when this Activity should be switched off. | |
| void | setTimeSpec (const TimeSpec &ts) |
| Supply a periodic time specification to the activity. | |
| void | changePriority (const PrioritySpec &s) |
| Change the priority spec. | |
| void | print (ostream &os) |
| Print to stream, for debugging purposes. | |
| int | noScheduledBehind () const |
| Find out how many more instances of this activity are scheduled. | |
| int | numScheduledBehind () const |
| Find out how many more instances of this activity are scheduled. | |
| TimingCheck * | getCheck () |
| Return a pointer to the check associated with this activity. | |
| const vstring & | getName () const |
| Return the name of the activity. | |
| const std::string & | getTargetName () const |
| As an activity target. | |
| void | logBlockingWait () |
| If your activity does blocking waits (file io etc.), it might be neat to report that, so that logging facilities can correctly interpret run times. | |
| void | logBlockingWaitOver () |
| Report that the blocking wait is over. | |
| bool | firstCycle (const TimeSpec &ts=TimeSpec(0, 0)) |
| Is this the first run after the activity has been switched on? | |
| bool | lastCycle (const TimeSpec &ts=TimeSpec(0, 0)) |
| Is this the last cycle before the activity will be switched off? | |
| bool | isBraking () |
| Indicate that the system has been commanded to stop. | |
Public Attributes | |
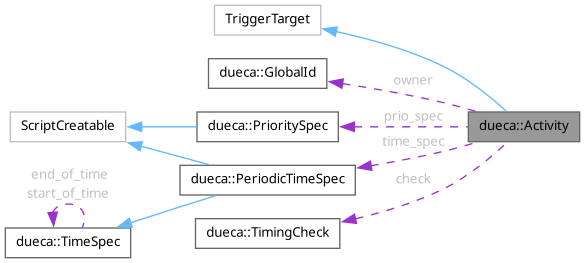
| GlobalId | owner |
| Owner of this activity. | |
| int | activity_id |
| Integer handle, unique within a node. | |
| PrioritySpec | prio_spec |
| Priority of the activity. | |
| RunState | run_state |
| Runstate of the activity, to save cycles on switch logic. | |
| TimeTickType | switch_on |
| Indicates the time from which this activity is switched on. | |
| TimeTickType | switch_off |
| Indicates the time until which this activity is switched on. | |
| PeriodicTimeSpec * | time_spec |
| Periodic timing specification for this activity. | |
| TimingCheck * | check |
| Pointer to a TimingCheck object. | |
| ActivityManager * | my_manager |
| A pointer to this activity's ActivityManager. | |
| int | no_schedules |
| Count of the number of times the activity has been scheduled. | |
| int | no_despatches |
| Count of the number of times the activity has been run. | |
| vstring | name |
| string format name. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | despatch (const TimeSpec &t)=0 |
| Invoke the activity. | |
| int | getOrder () const |
| Return the "order" part of the priority. | |
| const GlobalId & | getOwner () |
| Return the id of the owner of the activity. | |
| bool | isInRunPeriod (const DataTimeSpec &ts) |
| Test whether activation is appropriate. | |
| DataTimeSpec | trimToRunPeriod (const DataTimeSpec &ts) |
| Trim a time spec to the run period. | |
| unsigned int | getDescriptionId () const |
| Return the id of the activity. | |
| void | trigger (const DataTimeSpec &t, unsigned idx) |
| Override of the trigger method from the TriggerTarget class. | |
Friends | |
| class | ActivityManager |
| class | ActivityItem |
| class | TimingCheck |
| Allow TimingCheck to use these functions. | |
Detailed Description
Activity objects represent a metafor for allocation of locus-of-control in DUECA.
DUECA is a data driven architecture, and many events (usually arrival of data, but also the passing of time), can lead to the situation where activities need to be performed/invoked. For anything to happen, an Activity needs to be created, and it needs to be connected to the events that trigger its scheduling. Once scheduled, it will be invoked by the ActivityManager. Whether this happens at once or later depends on the other Activities scheduled, and the importance of a specific Activity.
You could allocate an Activity by making a class derived from this one. However, this is not recommended. Instead, make a Callback object and use an ActivityCallback object.
Member Enumeration Documentation
◆ RunState
To track the run state, and signal about first/last/work etc.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| Off | Not running, initial state. |
| Last | Last activation with the current run span; for a CriticalActivity, last activation in the safe mode before stop. |
| Ready | Switch-on call happened, time for start set but not not yet running. For CriticalActivity, not yet running in safe mode. |
| Braking | SwitchOff call happened, close to stopping. |
| Running | Running, activated activity. |
| ReadyWork | Ready for a transition to the work state. |
| FirstWork | First cycle in work, CriticalActivity only. |
| RunningWork | Running in work mode, CriticalActivity only. |
| BrakingWork | switchSafe called, close to transition safe state |
| LastWork | last cycle in the work state |
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ Activity()
| dueca::Activity::Activity | ( | const GlobalId & | owner, |
| const char * | my_name, | ||
| const PrioritySpec & | s ) |
Constructor.
- Parameters
-
owner A DUECA named object should own this activity. my_name Descriptive name for the activity. s Priority specification.
Member Function Documentation
◆ despatch()
|
protectedpure virtual |
Invoke the activity.
This is called by the ActivityManager, via the ActivityItem that defined the activity.
◆ getOrder()
|
inlineprotected |
Return the "order" part of the priority.
This is used to determine which activity is more important.
◆ getDescriptionId()
|
inlineprotected |
Return the id of the activity.
This id is linked to the description.
◆ trigger()
|
protected |
Override of the trigger method from the TriggerTarget class.
When this method is called, the Activity schedules itself for invocation.
◆ switchOn() [1/2]
| void dueca::Activity::switchOn | ( | const TimeTickType & | time = 0 | ) |
Specify the time from which the Activity is switched on.
- Parameters
-
time Time from which to start.
◆ switchOff()
| void dueca::Activity::switchOff | ( | const TimeTickType & | time = 0 | ) |
Specify the time when this Activity should be switched off.
- Parameters
-
time Time at which to stop.
◆ switchOn() [2/2]
|
inline |
Specify the time from which the Activity is switched on.
- Parameters
-
time The start of this time specification defines start of the activity .
◆ noScheduledBehind()
|
inline |
Find out how many more instances of this activity are scheduled.
This can be used in display drawing modules, to exit and eliminate a backlog in drawing calls and updates.
◆ numScheduledBehind()
|
inline |
Find out how many more instances of this activity are scheduled.
This can be used in display drawing modules, to exit and eliminate a backlog in drawing calls and updates.
◆ getCheck()
|
inline |
Return a pointer to the check associated with this activity.
Might return NULL!.
◆ firstCycle()
Is this the first run after the activity has been switched on?
Note that this tests on the TimeSpec, it works with clock or stream channel driven activities with regular activation, it might mis-fire on activities driven by event channels.
◆ lastCycle()
Is this the last cycle before the activity will be switched off?
Note that this tests on the TimeSpec, it works with clock or stream channel driven activities with regular activation, it might mis-fire on activities driven by event channels.
Member Data Documentation
◆ owner
| GlobalId dueca::Activity::owner |
Owner of this activity.
The owner is generally the one who made and uses the activity.
◆ activity_id
| int dueca::Activity::activity_id |
Integer handle, unique within a node.
This id is used for logging purposes
◆ prio_spec
| PrioritySpec dueca::Activity::prio_spec |
Priority of the activity.
The priority determines by which ActivityManager the Activity is handled. It also contains a member for the order, which determines which of the Activities handled by this ActivityManager is more important.
◆ switch_on
| TimeTickType dueca::Activity::switch_on |
Indicates the time from which this activity is switched on.
If one tries to schedule the activity for a time smaller than this, the activity is not scheduled.
◆ switch_off
| TimeTickType dueca::Activity::switch_off |
Indicates the time until which this activity is switched on.
If one tries to schedule the activity for a time later than this, the activity is not scheduled.
◆ time_spec
| PeriodicTimeSpec* dueca::Activity::time_spec |
Periodic timing specification for this activity.
If present, this timing specification is combined with the timing specification with which the activity was triggered. This produces regular invocations with the offset and period specified in this time_spec, instead of invocations determined by the validity start and span of the incoming data.
◆ check
| TimingCheck* dueca::Activity::check |
Pointer to a TimingCheck object.
If not NULL, this TimingCheck will check and periodically send timing results.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- /home/abuild/rpmbuild/BUILD/dueca-4.2.5-build/dueca-4.2.5/dueca/Activity.hxx